
Connet CoSF-D is a low-noise Single Frequency Fiber Laser based on Distributed Feedback Bragg Grating (DFB) technology. It has independent intellectual property rights and achieves a stable single-frequency laser output with single longitudinal mode, linear polarization, and narrow linewidth.
CoSF-D has very low phase and frequency noise and low relative intensity noise (RIN). Connet uses unique packaging technology to ensure low-noise DFB single frequency fiber lasers with excellent wavelength stability.
Connet uses extra-cavity technology to significantly suppress the relative intensity noise (RIN) of the DFB single frequency fiber laser, ensuring that the resonant cavity of the single frequency fiber laser is not disturbed.
CoSF-D Mini Narrow Linewidth Single Frequency Fiber Laser has a small compact size of 110x70x25mm with the sturdy package and output power of up to 20mW.
Features:
Applications:
Test Data:
|
Parameter |
Test Result |
|
Center wavelength |
1549.73nm |
|
Output power |
20mW |
|
Linewidth |
8kHz |
|
SMSR |
55.46dB |
|
Beam quality |
<1.05 |
|
RIN peak frequency |
~1300kHz |
|
RIN peak |
~ -133dBc/Hz |
|
RIN@10MHz |
<-140dBc/Hz |
|
PER |
>25dB |
|
Output isolation |
>32dB |
|
Output power stability (RMS) |
<1% |
|
Operating temperature |
0-50℃ |
|
Storage temperature |
-20-65℃ |
|
Optical spectrum |
Fig. 1 |
|
Beat frequency spectrum |
Fig. 2 |
|
RIN |
Fig. 3 |
|
Phase noise |
Fig. 4 |
Product Information:
|
Product |
CoSF-D Mini Narrow Linewidth Single Frequency Fiber Laser |
|
P/N |
CoSF-D-RS-EY-Mini |
|
Operation mode |
CW, Single Frequency, Single Longitudinal Mode |
|
Output fiber |
1m PM1550-XP, 0.9mm jacket, FC/APC connector |
|
Monitor fiber |
Optional |
|
Dimension |
110x70x25mm |
|
Control interface |
RS485 |
Test Environment and Power Supply:
|
Parameter |
Specification |
|
Power Supply |
+12VDC, 1A |
|
Test Temperature |
25℃ |
|
Humidity |
<90% |
|
Warming-up Time |
<mins |
Schematic Diagram of Test:
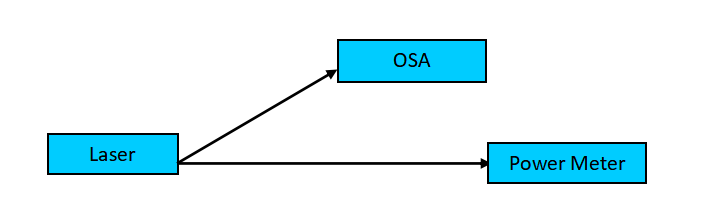
Schematic Diagram of Spectrum Measurement
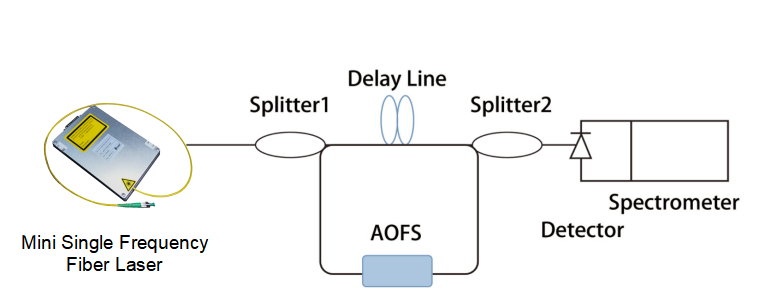
Schematic Diagram of Linewidth Measurement
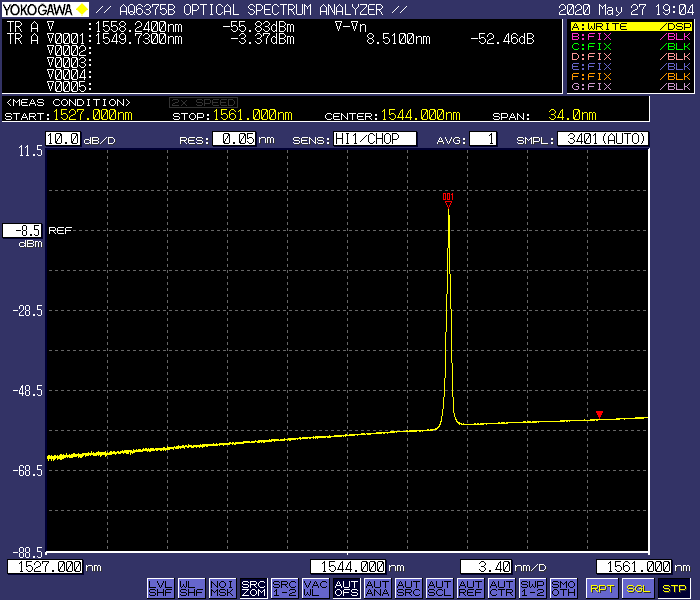
Fig. 1 Optical Spectrum
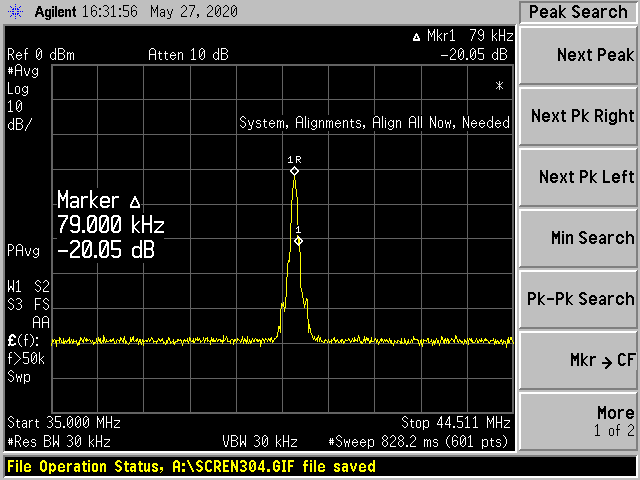
Fig. 2 Beat Frequency Spectrum
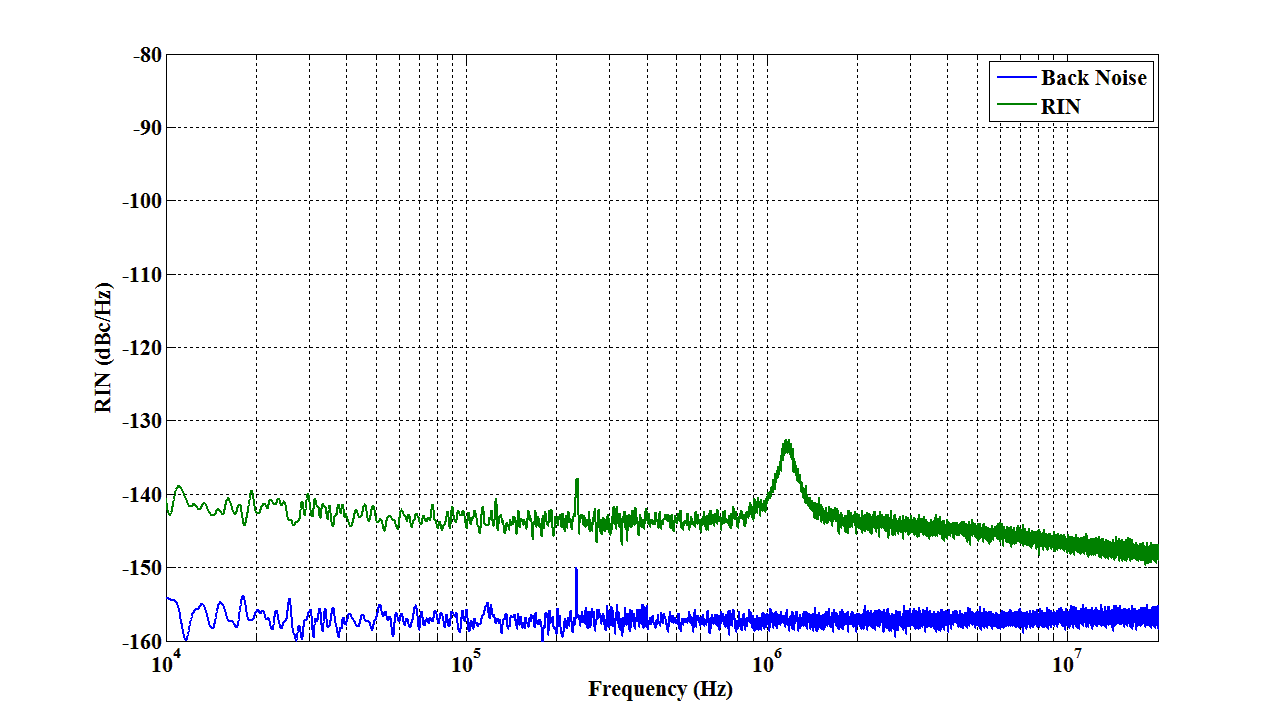
Fig. 3 RIN
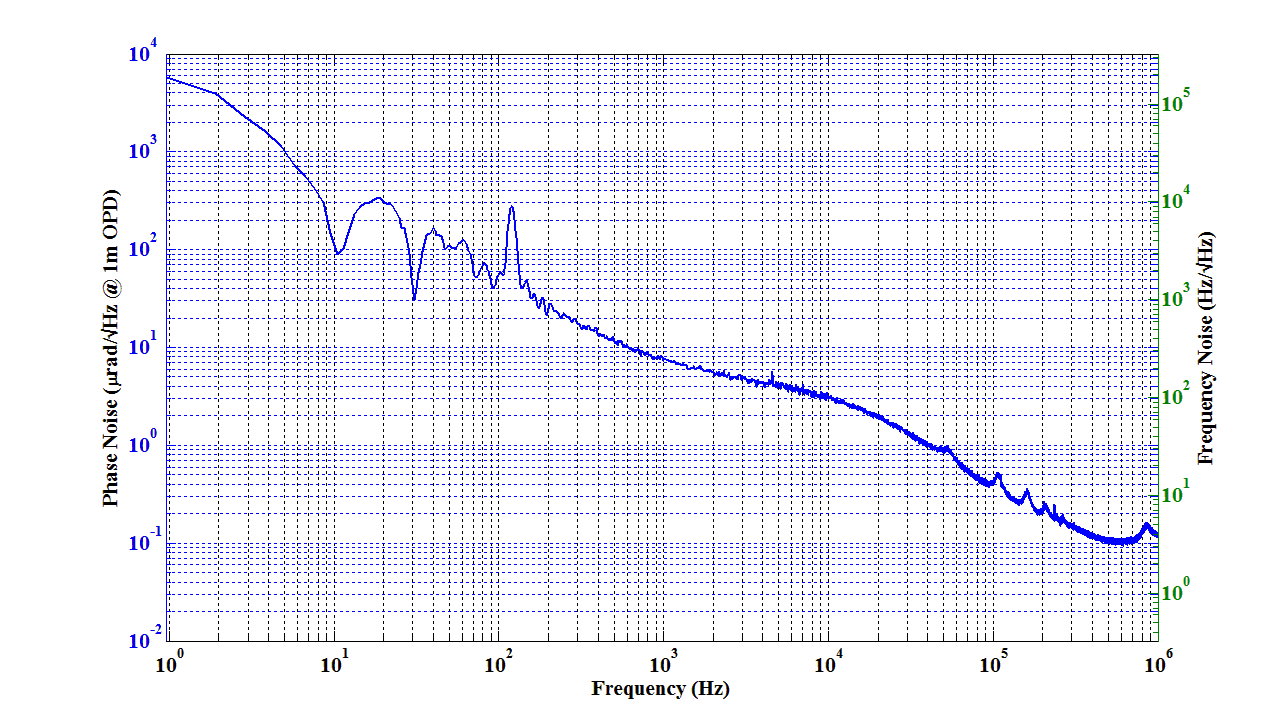
Fig. 4 Phase Noise